

From CDC Mid Year Report 1999
AIDS incidence decreased 18% between 1996 and 1997. From 1997 to 1998, AIDS incidence decreased 11%, suggesting that the decrease in AIDS incidence is slowing. The slowing in the decrease in AIDS incidence is paralleled by a slowing in the decrease in the number of AIDS deaths. Deaths decreased 42% from 1996 to 1997, and 20% from 1997 to 1998. The number of persons living with AIDS continues to increase.
At the end of 1997 there were 269,777 persons living with AIDS. By the end of 1998, there were 297,137 persons living with AIDS, a 10% increase. The decreases in AIDS incidence and the number of AIDS deaths, first noted in 1996, have been ascribed to the effect of new treatments. Although a substantial decline in AIDS incidence continues, the slowing rate of the decline may indicate that much of the benefit of new therapies has been realized. Most persons in care may now be receiving effective therapies. In addition, the duration of the effect of treatment may be limited for some persons. In 1996, decreases were noted in the number of deaths before they were noted in AIDS incidence because persons with the most advanced disease were the first to benefit from the new treatments. Persons with more advanced disease may experience improved health as a result of treatments for a shorter time than others do. Incomplete adherence to treatment schedules and viral resistance may also be contributing factors. Information on the diagnosis and treatment of persons with HIV will improve our understanding of the current HIV epidemic, and most of the persons who now have AIDS may be persons who first received a diagnosis of HIV infection when they became ill with AIDS, or who were not receiving treatment for HIV infection. Supplemental information will be collected on samples of AIDS cases and deaths in order to better understand the trends.
From July 1998 through June 1999, a total of 47,083 AIDS cases were reported, compared with 54,140 and 64,597 cases reported in the two preceding
12 month periods, July 1997 through June 1998 and July 1996 through June 1997. Despite the continued decease in the number of cases reported, state and local health departments continue to report a large number of AIDS cases. Women account for 10,841 (23%) reported adult cases. Among women, blacks and Hispanics account for 80% of cases; among men, blacks and Hispanics account for 61% of cases.Women account for 32% of adult cases of HIV infection reported from July 1998 through June 1999. Among women, blacks and Hispanics account for 77% of cases; among men, blacks and Hispanics account for 58% of cases. Persons aged 13-24 account for 15% of reported HIV cases, and women account for 49% of cases in this age group. Risk information is difficult to interpret because of the high proportion of cases reported without risk. Several projects are under way to improve the risk information in the HIV data.
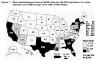 Male adult/adolescent annual AIDS rates, United States, July 1998-June
1999 From CDC
Male adult/adolescent annual AIDS rates, United States, July 1998-June
1999 From CDC
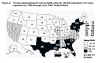 Female adult/adolescent annual AIDS rates, United States, July 1998-June
1999 From CDC
Female adult/adolescent annual AIDS rates, United States, July 1998-June
1999 From CDC
Read the full report
HIV/AIDS SURVEILLANCE REPORT, 1999 MIDYEAR EDITION (requires Acrobat)