| xx | xx | ||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
| BACTERIOLOGY | IMMUNOLOGY | MYCOLOGY | PARASITOLOGY | VIROLOGY | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Let us know what you think |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
| Logo image © Jeffrey Nelson, Rush University, Chicago, Illinois and The MicrobeLibrary | |||||||||||||||||||||||
|
TEACHING
OBJECTIVES |
Malignant Transformation The proliferation of normal cells is carefully regulated. However, such cells when exposed to chemical carcinogens, irradiation and certain viruses may undergo mutations leading to their transformation into cells that are capable of uncontrolled growth, producing a tumor or neoplasm. A tumor may be:
Evidence for immune reactivity to tumors There is a lot of evidence that tumors can elicit an immune response. Such evidence includes:
Tumor associated antigens In order for the immune system to react against a tumor, the latter must have antigens that are recognized as foreign. A number of alterations in gene expression occur in cells during tumorigenesis. Tumorigenesis may lead to expression of new antigens (neoantigens) or alteration in existing antigens that are found on normal cells. These antigens may include membrane receptors, regulators of cell cycle and apoptosis, or molecules involved in signal transduction pathways. There are 2 main types of tumor antigens:
Although chemical- , UV- or virus-induced tumors express neo-antigens, the majority of these tumors are often weakly immunogenic or non-immunogenic. In most cases, TSTAs cannot be identified easily. Some of these antigens may be secreted while others may be membrane-associated molecules.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
 Figure 1
Figure 1 |
Tumor associated transplantation antigens on viral tumors Viruses that cause human tumors include: DNA viruses
RNA viruses
A number of viruses cause different types of tumors in animals (for example, SV-40 virus, adenovirus, Rous sarcoma virus, Friend erythroleukemic virus, Moloney Rauscher and Gross viruses). Viruses are involved or suspected to be involved in some human malignancies (HTLV-1 in leukemia, hepatitis-B virus in hepatic carcinoma, papilloma virus in cervical cancer). Virus-induced tumors express cell surface antigens (distinct from antigens of the virion itself) which are shared by all tumors induced by the same virus. These antigens are characteristic of the tumor-inducing virus, regardless of tissue origin of the tumor or animal species in which the tumor exists (Figure 1). More information on tumor viruses can be found in the section on oncogenic viruses
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
 Figure 2
Figure 2 |
Tumor associated transplantation antigens on chemically-induced tumors Chemically-induced tumors are different from virally-induced tumors in that they are extremely heterogeneous in their antigenic characteristics. Thus, any two tumors induced by the same chemical, even in the same animal, rarely share common tumor specific antigens (Figure 2). These unique antigens on chemically-induced tumors are referred to as tumor specific transplantation antigens (TSTA).
Syngeneic, Allogeneic and Xenogeneic Tumors A tumor that grows in an animal strain will also grow in another animal belonging to the same inbred strain obtained by repeated brother-sister matings. These animals express the same MHC molecules and are referred to as syngeneic. However, most normal animal populations are allogeneic and have various MHC haplotypes. Thus, a tumor transferred from one animal to another animal belonging to an outbred strain is rejected because of the allo-MHC rather than the TSTA. A tumor transferred from an animal belonging to one species to another animal belonging to a different species is rapidly rejected because the animals are xenogeneic.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Immunity against tumors Although there is ample evidence for anti-tumor immune reactivity in humans, evidence for immunity against malignancy comes mostly from experimental studies with animals. In these, mice were immunized by administering irradiated tumor cells or following removal of a primary tumor challenged with the same live tumor. These animals were found to be resistant to rechallenge with the same live tumor. While antibodies may develop against few cancers, cell-mediated immunity plays a critical role in tumor rejection. Thus, immunity can be transferred, in most cases, from an animal, in which a tumor has regressed, to a naive syngeneic recipient by administration of T lymphocytes. The T helper (Th) cells recognize the tumor antigens that may be shed from tumors and internalized, processed and presented in association with class II MHC on antigen presenting cells. These Th cells, when activated, will produce cytokines. Thus, the Th cells provide help to B cells in antibody production. Cytokines such as IFN-gamma may also activate macrophages to be tumoricidal. Furthermore, the Th cells also provide help to tumor-specific cytotoxic T cells (CTLs) by inducing their proliferation and differentiation. The CTLs recognize tumor antigens in the context of class I MHC and mediate tumor cell lysis. In tumors that exhibit decreased MHC antigens, natural killer (NK) cells are important in mediating tumor rejection.
Escape from immuno-surveillance According to the Immune Surveillance Theory, cancer cells that arise in the body are eliminated by the immune system. However, due to impaired immune reactivity, cancer cells may escape destruction. Tumors evade immune recognition by several mechanisms. Tumors may not express neo-antigens that are immunogenic or they may fail to express co-stimulatory molecules required for the activation of T cells. In addition, certain tumors are known to lack or be poor expressers of MHC antigen. Another reason for failure of immune surveillance may be the fact that in the early development of a tumor, the amount of antigen may be too small to stimulate the immune system (low dose tolerance) or, due to the rapid proliferation of malignant cells (high dose tolerance), the immune system is quickly overwhelmed. In addition, some tumors may evade the immune system by secreting immunosuppressive molecules and others may induce regulatory cells particularly the CD4+CD25+ FoxP3+ T regulatory cells. Also, some tumors may shed their antigens which in turn may interact and block antibodies and T cells from reacting with the tumor cells.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Use of tumor neo-antigens in patient management The presence of neo-antigens on tumor cells has been exploited for both diagnostic and therapeutic purposes.
Monoclonal antibodies labeled with radioisotope have been used for in vivo detection of relatively small tumor foci. Antibodies have also been used in vitro to identify the cell origin of undifferentiated tumors, particularly of lymphocytic origin. Also, immuno-histological staining is used to confirm suspected metastatic foci, especially in bone marrow.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
Immunotherapy has been used as a novel means of treating cancer. Both active and passive means of stimulating the non-specific and specific immune systems have been employed, in some cases with significant success.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
A variety of immunopotentiating
agents (biological response modifiers) are used to enhance anti-tumor immunity.
They include bacterial products, synthetic chemicals and cytokines (Table 2).
Most of these agents exert their effects by activating macrophages and natural
killer (NK) cells,
eliciting cytokines or enhancing T-cell functions.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
| A number of cytokines have been
used to potentiate the immune function of the host since the discovery that
these cytokines have potent and selective effects on certain components of the
immune system (Table 3).
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
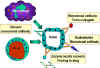 Figure 3
Figure 3 |
Monoclonal anti-tumor antibodies have been used in different forms for the treatment of cancer, either because of their direct effect or as vehicles to target anti-cancer drugs, toxins and the non-specific components of the host's immune system to the site of tumor (Figure 3). In addition, such specific antibodies are also used in the diagnosis of metastatic lesions, otherwise not detectable by conventional radiologic means. | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
